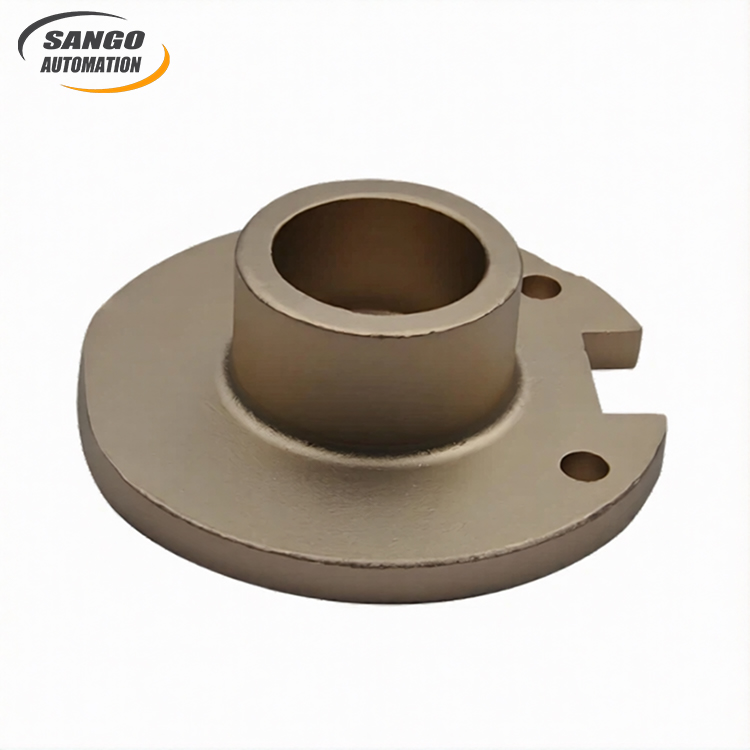
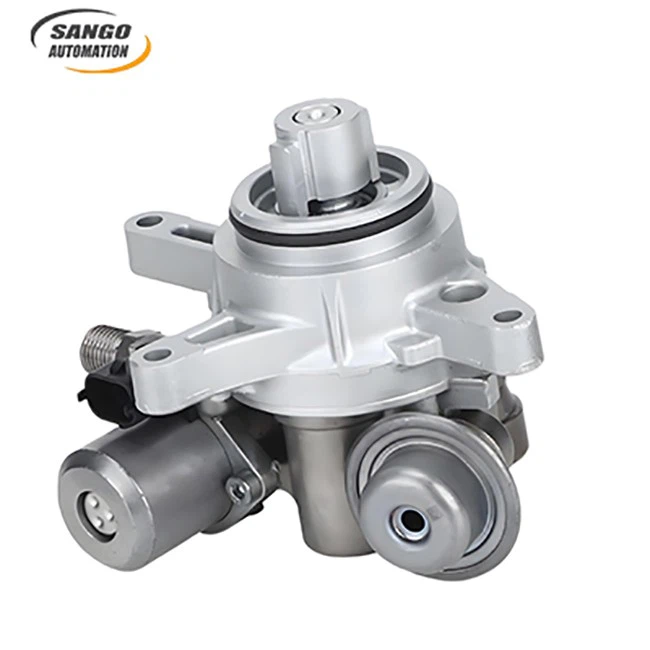
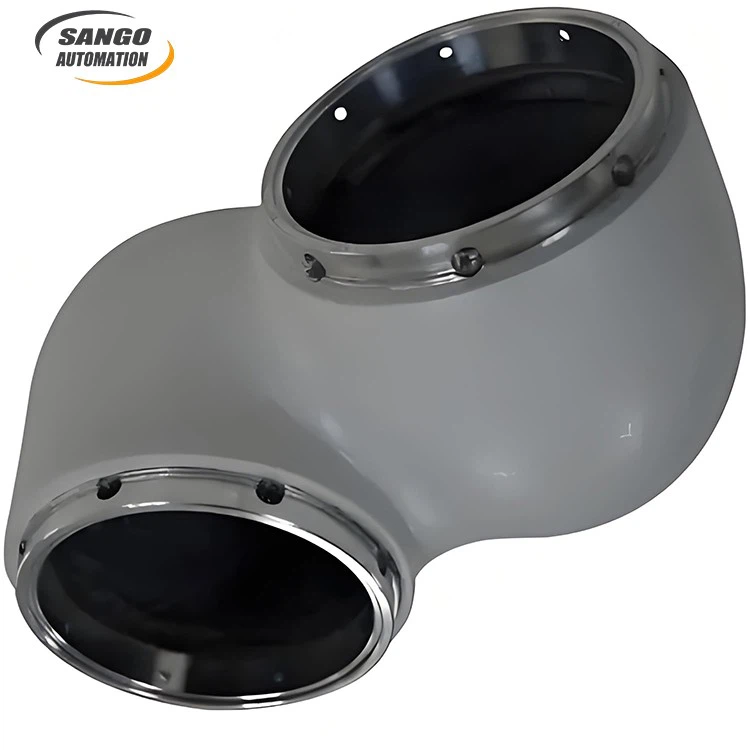
About Copper Casting
Product Feature
Excellent electrical and thermal conductivity
Copper casting shows excellent properties of copper material itself, including excellent electrical conductivity and thermal conductivity, which makes copper castings perform well in situations that require efficient conduction of heat or electrical.
High hardness and good wear resistance
Copper casting has excellent properties of casting and cutting properties and good corrosion resistance in the atmosphere and fresh water. It can be used for worn parts during operation under high loads (below 20Mpa) and high sliding speeds (8m/s), such as connecting rods, bushings, bearing shells, gears, worm wheels, etc.
Good corrosion resistance
It can resist the erosion of various chemical substances and prolong the service life.
Easy to process
Copper casting can be fabricated into various shapes and sizes through processes such as drilling, grinding, and turning to meet diverse design requirements.
Classification
| Type |
Material |
| Pure copper casting |
Made from pure copper (red copper) It features excellent electrical conductivity, thermal conductivity and corrosion resistance, and is often used in electronic components, chemical equipment and other fields. |
| Copper alloy casting |
Alloys with different properties are formed by adding other metal elements (such as tin, aluminum, zinc, etc.), mainly including:
Tin bronze (such as ZCuSn10P1) : It has high wear resistance and is suitable for high-load parts (such as bearing shells and gears).
Aluminum bronze: High strength and corrosion resistance, used in ships and chemical machinery.
Brass (such as ZCuZn series) : Easy to process, often used in valves and decorative parts. Phosphor bronze and beryllium bronze: High hardness and fatigue resistance, used in precision instruments and high-temperature environments. |
| Type |
Forming method |
| Sand casting |
It is suitable for complex-shaped and large-sized castings, accounting for more than 80% of the total output of copper castings. |
| Metal mold casting |
High-precision and high-efficiency production is achieved through metal molds, which are mostly used for precision parts. |
| Centrifugal casting |
It is used for the production of ring-shaped or cylindrical castings (such as copper sleeves and copper rings), which can enhance the density of the material. |
| Die casting |
It is suitable for small and precision parts of non-ferrous metals such as aluminum, magnesium and zinc, with high production efficiency. |
| Other processes |
Including investment casting (for complex thin-walled parts), continuous casting (for long strip-shaped billets), etc. |
Process parameters
| Parameters |
Description |
| Machining allowance |
In order to ensure the machining surface size of the casting and part accuracy, the thickness of the metal layer is increased in advance during the process of casting design and be cut off during mechanical processing. |
| Linear shrinkage |
Affected by alloy type, casting cooling, shrinkage resistance and other factors. |
| Demolding slope |
parallel to the slope of demolding direction which is on the pattern or core box wall. |
| The size of the minimum Casting hole |
The minimum hole diameter of the casting |
| Molding allowance |
The additional amount specially required during casting and cutting processing |
| Joint allowance |
In the subdivision design of castings, the negative number designed in advance in order to facilitate casting and processing. |
| Anti-deformation amount |
The amount of deformation generated by cooling of casting during the casting process. |
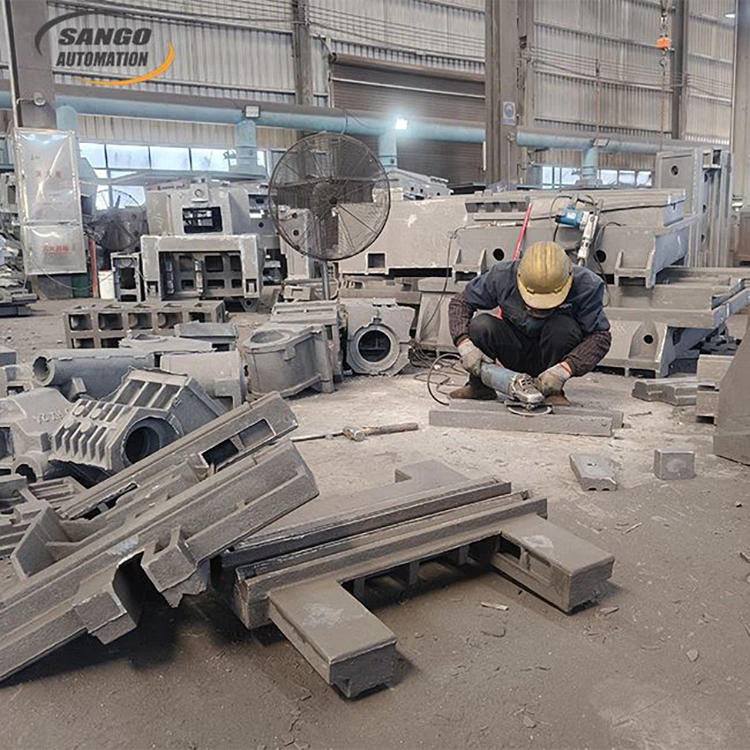
Process
Material selection
It is of great significance for material selection of copper casting. There are a great variety of copper alloys. Different alloy compositions can affect the mechanical properties, corrosion resistance and processing characteristics of castings. Common copper alloys include brass, bronze, etc. Each alloy has its specific application scenarios.
Design and manufacture of molds
The design and manufacture of molds are key links in the production of copper casting. The quality of the mold directly determines the precision and surface quality of the casting. Computer-aided design (CAD) and computer-aided manufacturing (CAM) technologies are usually adopted to optimize mold structures and enhance production efficiency.
Melting and pouring
The processes of melting and pouring require control precisely. The melting point of copper alloys is relatively high, and the requirements for melting equipment are also quite strict. The manufacturer will use advanced melting furnaces and strictly control the melting temperature and time to ensure the uniformity and purity of the alloy composition. In order to avoid defects such as pores and shrinkage cavities, it is necessary to control the pouring speed and temperature well during pouring.
Post-processing procedure
The post-treatment process also has a significant impact on the final quality of copper casting. In order to remove burrs and oxide layers on the surface, castings need to be cleaned, grinded, polished and other treatments after cooling. Heat treatment, surface coating and other processing may also be needed for some application scenarios with higher requirements. It will enhance the performance or aesthetic appearance of the castings.
Exceptional Quality and VersatilityEvery copper casting produced by us demonstrates supreme quality, making them a preferred choice in electronics, machinery, and architectural projects. We are committed to providing products that adhere to rigorous industry standards, ensuring performance and reliability in critical applications.
Comprehensive Service NetworkBased in India, our company operates as a distributor, exporter, manufacturer, supplier, and trader. This extensive network ensures efficient distribution and customer support across local and international markets. Clients benefit from our expertise and prompt service, backed by a 1-year warranty.
FAQ's of Copper Casting:
Q: How are your copper castings used in electronic, machinery, and architectural applications?
A: Our copper castings serve multiple roles across industries. In electronics, they are used for conducting electricity and heat. In machinery, the parts provide structural integrity and wear resistance. In architecture, copper is valued for its aesthetic appeal and corrosion resistance.
Q: What process do you follow to manufacture copper castings?
A: We utilize precision casting techniques, ensuring each copper component meets specific design and performance criteria. From raw material selection to final inspection, every stage is managed with strict quality controls, resulting in consistent, high-grade products.
Q: When should you consider using copper castings for your project?
A: Copper castings are most suitable when your project demands excellent thermal and conductive properties, durability, and resistance to corrosion. They are ideal for electronics, machinery parts, and decorative architectural elements when quality and longevity are priorities.
Q: Where are your copper castings manufactured and supplied from?
A: All our copper castings are manufactured in India. We supply both nationally and internationally, utilizing our roles as distributor, exporter, and supplier to reach diverse markets efficiently.
Q: What benefits do your copper castings provide over other materials?
A: Copper castings offer superior conductivity, excellent corrosion resistance, and long-lasting performance. Their unique properties make them more suitable for specialized applications compared to other materials, particularly where reliability is paramount.
Q: How do you ensure the quality of copper castings before distribution?
A: Each product undergoes thorough inspections and quality checks during and after manufacturing. Adhering to strict standards ensures that every casting delivered meets customer expectations for performance and reliability.
Q: Is there a warranty on your copper casting products?
A: Yes, all our copper castings include a 1-year warranty, covering manufacturing defects and assuring clients of our commitment to product quality and durability.
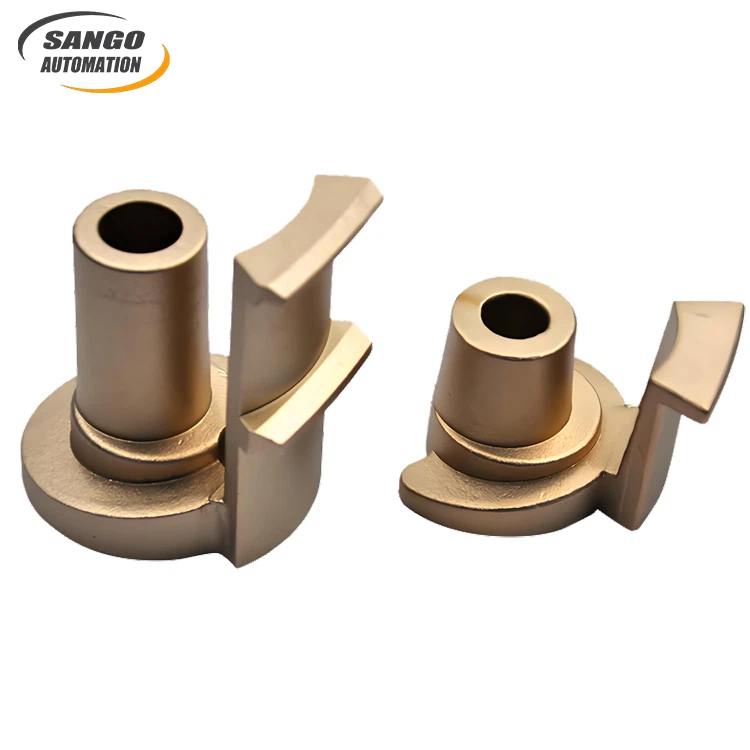
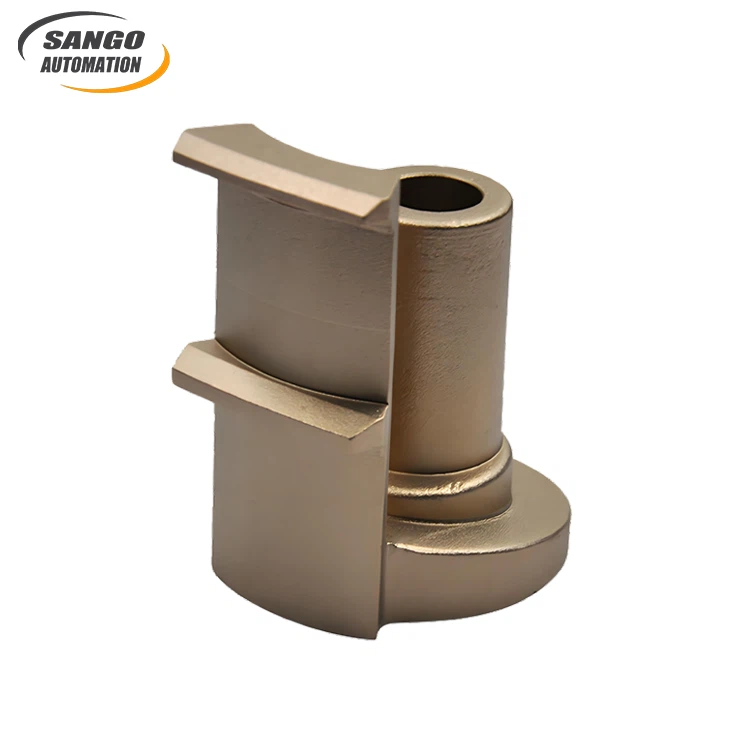
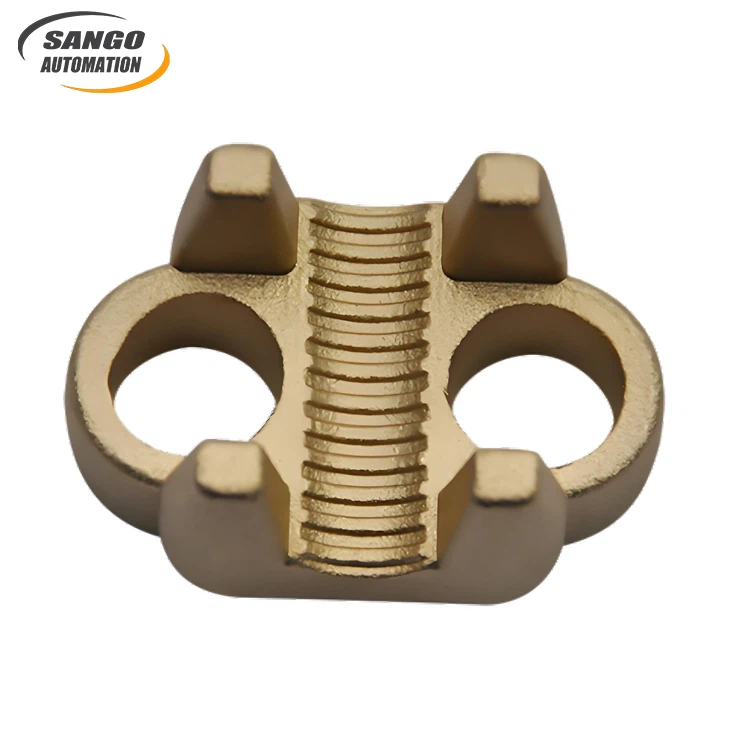




 Send Inquiry
Send Inquiry






 English
English Spanish
Spanish French
French German
German Italian
Italian Chinese (Simplified)
Chinese (Simplified) Japanese
Japanese Korean
Korean Arabic
Arabic Portuguese
Portuguese