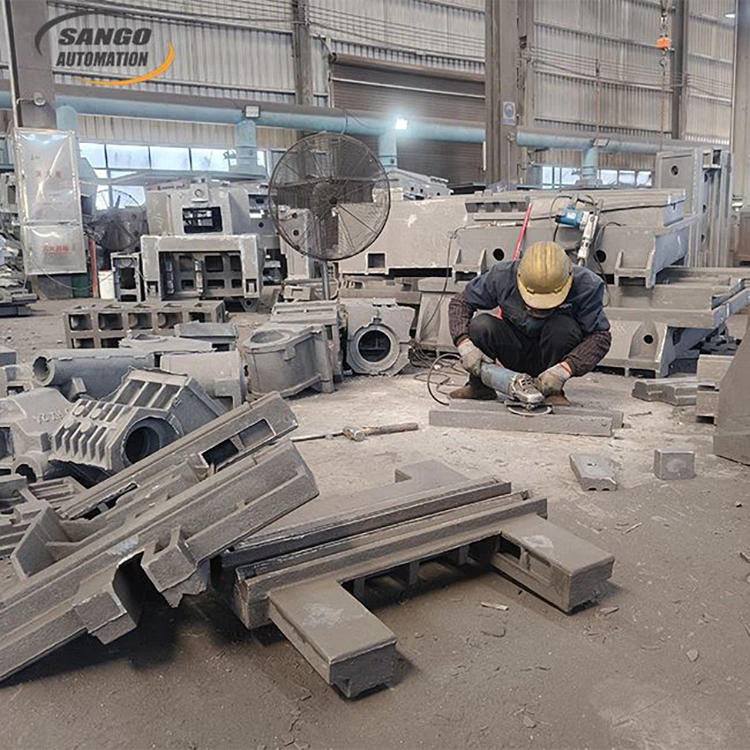
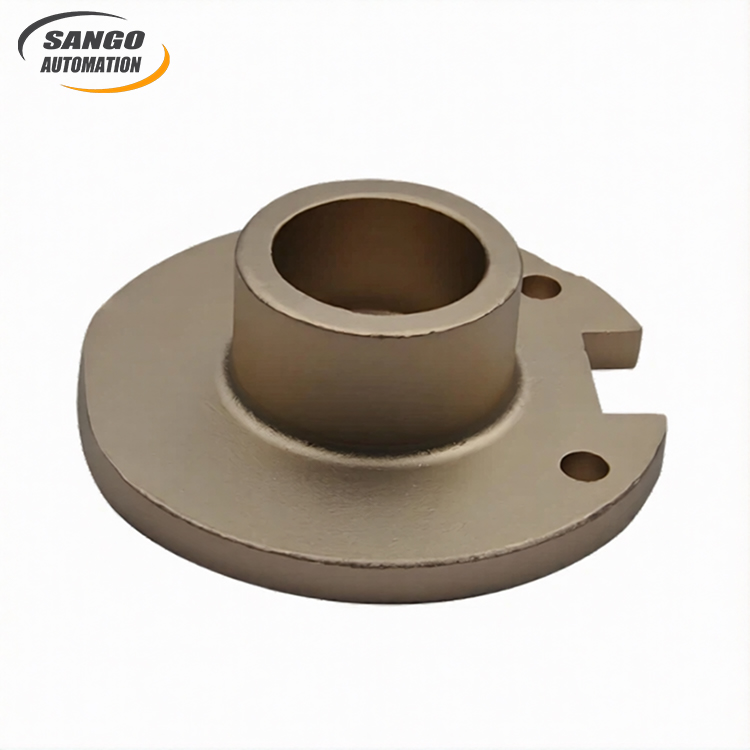
About Casting Iron Parts
Product Features
Casting iron parts can exhibit different characteristics depending on the type of material chosen (e.g., Ductile Cast Iron, Gray Cast Iron, White Cast Iron, etc.). In this module, I will focus on the common characteristics of casting iron parts from different materials.
Good Shock Absorption
Because graphite is present in the composition of various cast iron materials, and graphite can effectively absorb mechanical vibration energy, the shock absorption performance of casting iron parts is better than that of other casting parts.
High Compressive Strength
Casting iron parts have a high compressive strength, with compressive strength close to that of steel, and are suitable for structural parts that are subjected to pressure.
Good Wear Resistance
Because the graphite in the material is a good lubricant, the graphite chips generated during the friction process can play a role in reducing friction, so the overall wear resistance of casting iron parts is better.
Material Selection
We at Sango customize casting iron parts for customers There are two main materials, namely Gray cast iron and Ductile cast iron. Below I will briefly introduce the grades, differences and most suitable application scenarios of these two types of materials that we use most often in Sango.
|
Material
|
Gray Cast Iron
|
Ductile Cast Iron
|
|
Trademark
|
HT250
|
HT300
|
QT200
|
|
Metallographic Organization
|
Pearlite matrix + flake graphite
|
Pearlite matrix + flake graphite
|
Ferrite matrix + spherical graphite
|
|
Performance
|
Tensile strength: 250 MPa
Hardness: HB 180-250
Modulus of elasticity: 105-130 GPa
|
Tensile strength: 300 MPa
Hardness: HB 200-270
Modulus of elasticity: 110-135 GPa
|
Tensile strength: 200 MPa
Hardness: HB 170-230
Toughness: Better than the previous two
Modulus of elasticity: 90-110 GPa
|
|
Advantage
|
It has the lowest cost, excellent shock absorption, wear resistance, and good casting fluidity, making it easy to produce complex parts.
|
Good shock absorption, with higher strength, hardness and wear resistance than HT250.
|
It has steel-like toughness and elongation.
It has high strength and toughness, and can be subjected to certain machining and heat treatment.
|
|
Common Applications
|
It is suitable for medium-strength structural parts and wear-resistant parts, commonly used in machine beds, bases, cabinets, etc.
|
It is used in structural parts and wear parts with high strength requirements, such as heavy machine tool beds, cylinder blocks of large engines, large gearboxes, etc.
|
It is commonly used for parts that need to withstand impact, bending or deformation, such as automobile wheels, chassis parts, valve bodies, gears, crankshafts, etc.
|
Casting Process Selection
There are many casting methods to produce casting iron parts, such as sand casting, investment casting, lost foam casting, etc. Choosing the right casting process can solve our production problems while saving costs. Below I will briefly describe the casting process suitable for cast iron.
Sand Casting
Sand Casting first makes the same pattern as the shape of the part, then puts the mold into the upper and lower sand boxes for molding, then takes out the mold to align and fix the upper and lower sand boxes, and slowly injects molten metal liquid through the pre-designed gate, and after cooling, the sand can be obtained by falling the sand.
Investment Casting
Investment casting, also known as lost wax casting, has a core difference in the use of wax molds to prepare molds. First, a wax mold consistent with the part is made, and then the wax pattern is coated with a refractory coating to make the mold shell. After the shell is prepared, it is dewaxed, that is, the wax mold is melted, and a cavity is formed inside the shell that is consistent with the part. After roasting, molten metal can be injected into the mold shell, and the finished product can be obtained by crushing the mold shell after cooling.
Lost Foam Casting
Lost foam casting is to use EPS to make molds, coat the foam molds consistent with the product with a layer of refractory material, dry them into the sand box and fill them with sand and press them, and then inject molten metal liquid into the gate, after the metal liquid touches the foam mold, the foam quickly vaporizes, and then the metal liquid fills the space of the foam mold, wait for cooling and solidification to dig out the dry sand, and clean up to obtain the finished product.
Premium Iron Casting SolutionsWe specialize in providing standard-sized iron casting parts renowned for their structural integrity and reliability. Whether you are in need of replacement parts or components for new industrial machinery, our cast iron products are tailored to support your operational requirements with an assurance of long-term quality.
Comprehensive Warranty & SupportEnjoy peace of mind with our one-year warranty covering all standard iron parts. As a trusted manufacturer and supplier in India, we prioritize customer satisfaction by offering dedicated after-sales support, ensuring any concerns are addressed promptly and efficiently.
FAQ's of Casting Iron Parts:
Q: How are your casting iron parts manufactured?
A: Our casting iron parts are produced through a precision casting process using premium-grade iron. This method ensures uniformity in size and strength, providing reliable performance for various industrial uses.
Q: What standard sizes are available for your cast iron parts?
A: We offer a comprehensive range of standard sizes to accommodate the most common industrial applications. The dimensions are carefully selected to meet general usage requirements, enabling easy compatibility and replacement.
Q: When should I consider using iron casting parts from your company?
A: Our iron casting parts are ideal for use whenever durability, cost-effectiveness, and consistent quality are required. They are most commonly employed in mechanical, automotive, and industrial machinery maintenance and assembly.
Q: Where can I purchase your cast iron components?
A: You can purchase our products directly from us as we are a distributor, exporter, manufacturer, supplier, and trader based in India, serving both domestic and international clients. Please contact our sales team for detailed ordering information.
Q: What is the process for warranty claims on your iron casting parts?
A: If you encounter any issues covered under the one-year warranty, simply contact our customer support with proof of purchase. Our team will guide you through the claim process and arrange for repair or replacement as applicable.
Q: How should I use and maintain your iron casting parts?
A: To maximize the lifespan of our iron casting parts, ensure they are correctly installed in compatible machinery, avoid overloading, and perform regular maintenance checks for wear. Proper usage helps in maintaining operational efficiency.
Q: What are the key benefits of choosing your casting iron parts?
A: Choosing our casting iron parts assures you of good quality, durability, and value for money, backed by a one-year warranty. Being non-automated components, they are simple to use and maintain, making them suitable for a wide range of industrial settings.


 Send Inquiry
Send Inquiry






 English
English Spanish
Spanish French
French German
German Italian
Italian Chinese (Simplified)
Chinese (Simplified) Japanese
Japanese Korean
Korean Arabic
Arabic Portuguese
Portuguese