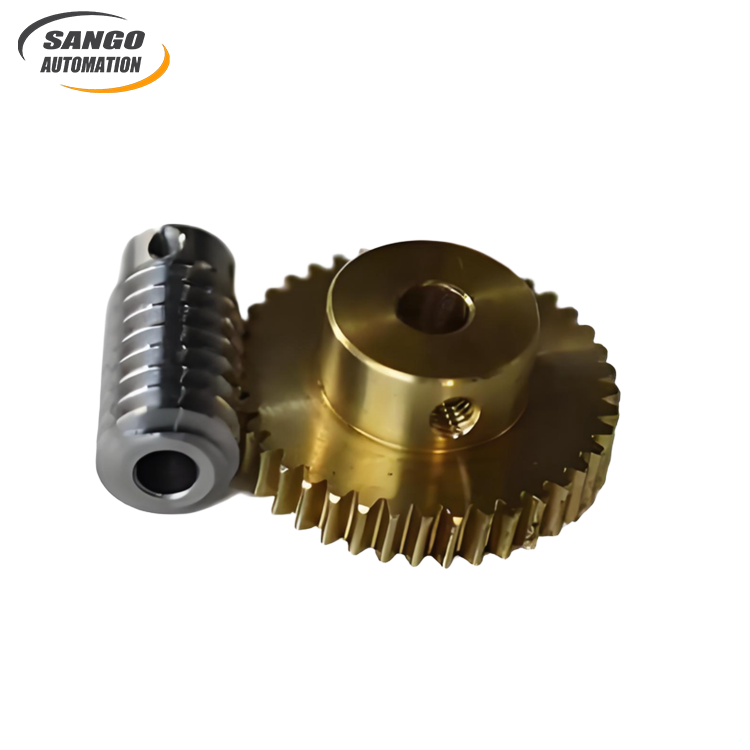
About Worm Wheel
Products Features
High Reduction ratio in a Small Package
Worm wheel can achieve high reduction ratios easily, sometimes up to 100:1. It can convert the power of high-speed rotation into low-speed and high-torque output, making it particularly suitable for small-space applications that require large torque.
Compact Design
Compact in structure, small in size, light in weight, and easy to install and maintain.
Compared with many traditional gear systems, worm wheel systems occupy less space due to their unique arrangement. This makes it suitable for applications where space is limited.
Self-Locking Functionality
When the lead Angle of the worm is less than the equivalent friction Angle between the meshing teeth, the mechanism has self-locking property. That is, only the worm can drive the worm wheel to rotate. This function is of great significance in many situations where reversal needs to be prevented. It greatly improves the reliability and stability of the equipment operation.
Smooth transmission and low noise
The design of the worm wheel and worm makes it run very smoothly with almost no vibration or noise, which is crucial for many industries.
Built for Strength and Longevity
Worm wheel are made from tough, wear-resistant materials, making them a long-lasting solution for heavy-duty work.
Friction and heat generation
The sliding action creates friction, which will reduce efficiency to 30-50%. The generated heat requires good lubrication to manage.
Process
Design and Planning
According to specific usage requirements and working conditions, determine the parameters of the worm wheel, such as module, number of teeth, helix Angle, center distance, etc.
Draw detailed processing drawings, including the shape, size and tolerance requirements of the worm wheel.
Material preparation
Select the appropriate material. Usually, the worm wheel is made of bronze or cast iron. Inspect the raw materials to ensure their quality meets the processing requirements.
Initial forming
Casting or forging: The basic shape of the worm wheel is first formed from a blank using casting or forging, especially for large-scale production.
Machining and finishing
Turning processing: Turn the blank of the worm gear to remove the excess material and process it into a rough shape and size. Then, the inner hole and end face of the worm gear are turned.
Milling: The initial shape of the tooth groove is machined.
Hobbing or shaping process: Further process the tooth profile to meet the precise meshing requirements.
Grinding processing: The tooth surface of the worm gear is ground to improve surface accuracy and smoothness and reduce tooth surface roughness.
Heat treatment and Surface treatment
According to the material and performance requirements, appropriate heat treatment should be carried out on the worm wheel and worm. It will increase its surface hardness, wear resistance, and lifespan.
Methods: Quenching, tempering, etc.
Surface treatmentinvolves anti-rust treatment of the worm wheel, such as galvanizing and oiling.
Quality control
Inspection: Dimensional and material inspections ensure the gear meets specifications. Use professional measuring tools, such as gear measuring instruments, to inspect parameters like tooth profile, tooth pitch, and center distance to ensure they meet the design tolerances.
Testing: The wheels are also tested under load to verify performance and reliability.
Durable Iron ConstructionManufactured with robust iron materials, our worm wheel and gear sets deliver exceptional strength and wear resistance, which is vital for intensive industrial usage. The iron composition enhances the gears' ability to handle significant loads and ensures longevity, minimizing the need for frequent replacements or downtime due to maintenance.
High Operational EfficiencyWith an efficiency rating of up to 90%, our worm gear systems maximize power transmission while minimizing energy loss. This makes them ideal for applications requiring smooth rotational motion, such as in conveyor belts or automated machinery, supporting productive and cost-effective operations.
Reliable Industrial SolutionsAs a reputable supplier and exporter from India, we adhere to stringent quality control measures to deliver consistent, high-performing products. Our broad distribution network guarantees timely delivery and technical support, ensuring seamless integration into your industrial processes.
FAQ's of Worm Wheel:
Q: How is the worm wheel with gear used in industrial applications?
A: The worm wheel with gear is primarily used to transmit power, reduce speed, and increase torque in various industrial machinery such as conveyor systems, lifts, and heavy-duty equipment. Its unique design enables smooth, controlled motion with minimal noise.
Q: What benefits does an iron worm gear provide for industrial usage?
A: Iron worm gears offer superior strength, wear resistance, and durability, making them ideal for harsh industrial environments. They withstand heavy loads and prolonged use, which helps reduce maintenance and extends the lifespan of the equipment.
Q: What is the efficiency level of this worm wheel, and how does it impact industrial operations?
A: The worm wheel boasts an efficiency of up to 90%, which means a significant portion of energy is effectively transferred, leading to better performance and reduced operational costs for industrial machinery.
Q: When should a worm wheel with iron gear be selected for an application?
A: A worm wheel with iron gear should be chosen when the application demands high load capacity, reliable operation, and superior wear resistance, especially in continuous or intensive industrial environments.
Q: Where are these worm wheels manufactured and supplied from?
A: These worm wheels are manufactured and supplied from India, utilizing advanced manufacturing processes to ensure high-quality standards and timely distribution to clients both domestically and internationally.
Q: What is the process for sourcing worm wheels from your company?
A: To source worm wheels, customers can contact us directly through our official channels. Our team will assist with product selection, pricing, and order placement, followed by prompt manufacturing and shipping according to your specifications.
Q: How does the use of a worm gear improve overall industrial performance?
A: Using a worm gear ensures efficient, smooth, and quiet operation in machinery. It also allows for substantial gear reduction and torque multiplication, enhancing machinery performance and energy efficiency in industrial settings.


 Send Inquiry
Send Inquiry






 English
English Spanish
Spanish French
French German
German Italian
Italian Chinese (Simplified)
Chinese (Simplified) Japanese
Japanese Korean
Korean Arabic
Arabic Portuguese
Portuguese