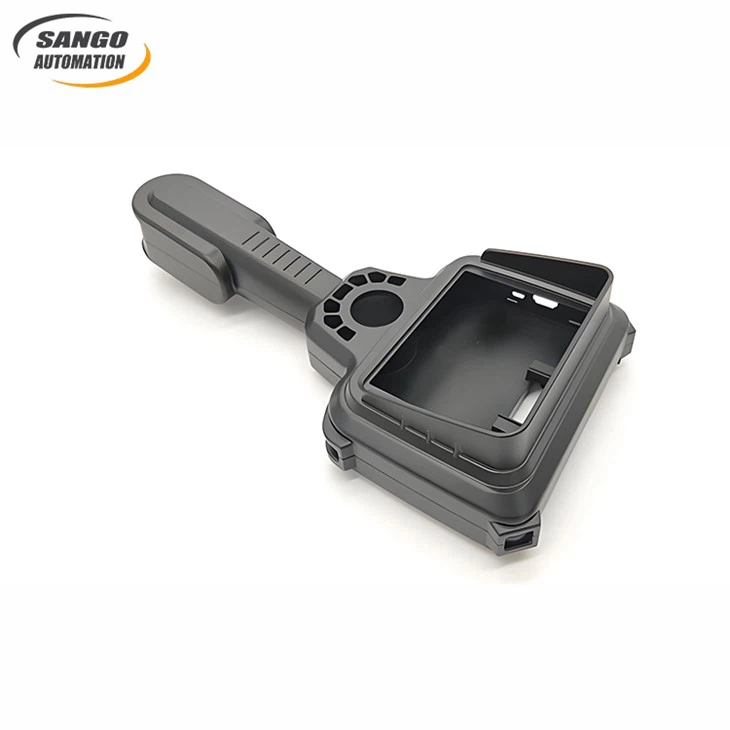
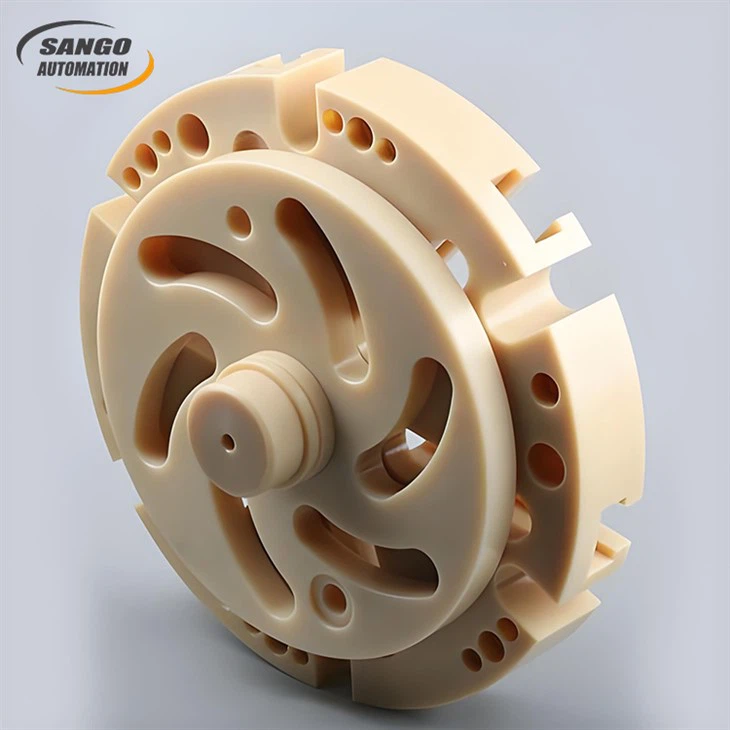
About CNC Plastic Machining
Features
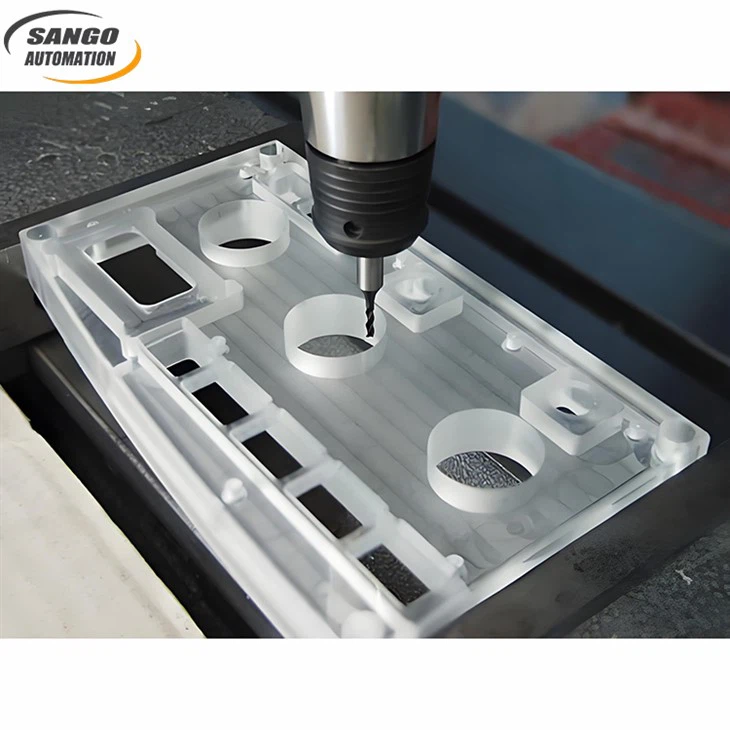
Precision Manufacturing
Our sango automation CNC machining service can achieve tight tolerances (0.05mm to 0.03mm or higher) and excellent surface finishes (capable of Ra0.8) to meet most customers' demanding applications for dimensional accuracy and appearance.
Wide Material Compatibility
We can process a wide range of plastic materials, such as ABS, polycarbonate (PC), acetal (POM), polyethylene (PE), PEEK, and acrylic (PMMA).
Complex Geometry
Our factory has a variety of machining equipment, such as CNC milling machines, four-axis and five-axis CNC machines, etc., and our CNC milling and turning capabilities can easily cope with complex 3D shapes, cavities, holes, threads, and fine features.
The process of plastic CNC machining
Requirements analysis and design review stage
The production process begins with a deep understanding of customer needs, and engineers review 3D models and 2D drawings based on part application scenarios (e.g., biocompatibility of medical devices, insulation of electronic components), focusing on assessing the unique processing risks of plastics: such as the tendency to deform of thin-walled structures, stress cracking that can be caused by sharp internal corners, and recommend the optimal material based on factors such as mechanical properties, chemical resistance, and cost (e.g., PEEK for aerospace parts, UV-resistant acrylic for transparent shells).
Programming and process planning phase
Based on the approved design, CAM engineers use specialized software to generate toolpaths. In view of the low melting point characteristics of plastics, the layered cutting strategy is forced to be used during programming (such as processing 10mm deep grooves in 4 times), and a compressed air cooling system is designed to replace the traditional cutting fluid. At the same time, large spiral angle diamond-coated tools are selected to reduce frictional heat, and vacuum adsorption fixtures are customized for easily deformed parts to control the processing deformation from the source.
Material pretreatment and clamping stage
Purchased plastic sheets/rods are subject to strict pretreatment: hygroscopic materials (e.g. nylon PA6) must be dehydrated in an oven at 80C for more than 24 hours. The clamping technique is used in step-by-step pressing technology - the blank is fixed with low torque first, the machine is suspended after roughing to recalibrate the clamping force, and a silicone buffer layer is applied to the contact surface to prevent dimensional drift caused by stress release during the finishing stage.
Core processing execution stage
High speed (18,000RPM) + fast feed (2m/min) for roughing and fast cutting allowance with 0.3mm finishing allowance reserved. The finishing phase is particularly critical: the use of a special polishing edge milling cutter, combined with a micron-level cutting depth (0.05-0.1mm) and a cooling air curtain, ensures that the cutting temperature is always lower than the material's glass transition point (e.g. PC material is controlled below 145C), while the high-pressure air gun purges chips in real time to prevent the molten plastic from re-bonding to the workpiece surface.
Real-time quality monitoring stage
During the machining process, online inspection is carried out for each completed key feature: laser displacement sensor is used to monitor the thin wall deformation, the key aperture is measured by a pneumatic gauge, the tolerance is required to 0.05mm mating surface, and the machine tool probe is started to scan the three-dimensional surface to ensure that thermal expansion does not lead to dimensional deviation.
Post-treatment and surface optimization stage
After the parts are offline, they undergo fine processing: microscopic burrs are manually removed with ceramic scrapers, and low-temperature plasma deburring technology is used for deep holes; Differentiated surface treatments are implemented according to functional requirements - the optical lens holder needs to be polished with diamond paste to Ra0.1m, while the friction parts are sandblasted to form an oil storage texture, and the acrylic edges are polished with hydrogen flame to achieve an optical transparency effect.
Final inspection and protective packaging stage
Perform full-scale verification on a coordinate measuring machine (CMM) and issue a test report with the batch number of the material. The packaging stage is strictly operated according to the material characteristics: static sensitive parts (such as semiconductor carriers) are vacuum-encapsulated with anti-static film, porous materials (such as UHMW-PE) are added with desiccant to prevent moisture absorption and deformation, and finally the honeycomb structure EPE foam is used to customize the transport tray to ensure the delivery of precision parts without damage.
Application
Medical Field
Electronics And Semiconductor
Aerospace & Transportation
Optics Industry
Industrial Equipment & Automation
Consumer Electronics
Precision in Every Plastic PartWe combine advanced CNC technology with high-grade plastic materials to manufacture parts that meet stringent industrial standards. Our standard sizes and variety of color options allow for versatile use across multiple sectors. Clients benefit from our focus on precision and consistency, ensuring each part is uniform and reliable. As an established player in the Indian market, we support industrial needs worldwide through exporting, distribution, and tailored customer service.
Comprehensive Service and Strong GuaranteeFrom design consultation to delivery, our team provides end-to-end support, ensuring clients receive the exact CNC plastic components they require. Each machined part undergoes rigorous quality checks before shipment. Our one-year warranty offers added confidence to customers, reflecting our dedication to quality and long-term performance. We serve as a dependable partner for industries looking for efficient, high-quality machining solutions.
FAQ's of CNC Plastic Machining:
Q: How does the CNC plastic machining process ensure high-quality industrial parts?
A: Our CNC plastic machining process relies on computer-controlled equipment to achieve precise dimensions and consistent finishes. By using premium plastic materials, we deliver components that meet rigid industrial quality standards for durability and performance.
Q: What standard sizes are available for CNC plastic machined parts?
A: We offer an array of standard sizes to cater to typical industrial requirements. This ensures compatibility and easy integration into existing systems, though specific customizations can be discussed based on project needs.
Q: When should industries consider using CNC machined plastic components?
A: Industries should opt for CNC machined plastic components when precise tolerances, repeatability, and efficient production are priorities-particularly in applications where good quality and reliability are required.
Q: Where are your CNC plastic machining services available?
A: Our CNC plastic machining services are available both across India and internationally. As a prominent distributor, exporter, manufacturer, supplier, and trader, we manage domestic and overseas orders efficiently.
Q: What are the main uses of CNC machined plastic parts in industrial settings?
A: CNC machined plastic parts are widely used in automotive, electronics, packaging, medical device manufacturing, and more, offering versatility thanks to robust material properties and adaptable designs.
Q: What benefits do customers receive from your CNC plastic machining services?
A: Customers benefit from superior quality, swift turnaround times, multiple color options, and comprehensive after-sales support. Additionally, a one-year warranty is provided on each part, ensuring peace of mind and long-term value.
Q: How can clients start the process of ordering CNC plastic machined parts?
A: Clients can initiate the process by reaching out with their requirements. Our experts will assist in selecting appropriate materials, dimensions, and finishes to ensure the final product aligns with even the most demanding industrial standards.




 Send Inquiry
Send Inquiry






 English
English Spanish
Spanish French
French German
German Italian
Italian Chinese (Simplified)
Chinese (Simplified) Japanese
Japanese Korean
Korean Arabic
Arabic Portuguese
Portuguese